Git support enabled on our servers
Providing a dev-friendly web hosting service is a must for each hosting company if they want to stay on top of this ever-evolving market.
With the evolution of application development, the need for setting up online dev environments on a web host has become a necessity.
One of the most popular dev instruments – Git, which every 4 out of 5 developers will expect you to provide, is now enabled on our web hosting platform.
What is Git about?
Created by Linus Torvalds – the author of the Linux kernel, Git is a popular distributed version control system used for software development purposes.
He jokingly named it “Git” – a British slang word for an “unpleasant person”.
As a version control system, Git manages and stores revisions of all types of projects, including code files, text files, image files, etc.
It keeps “snapshots” of every change in the project’s history, so you never risk losing or overwriting anything.
In contrast to its predecessors such as CVS and SVN where all changes are committed to a central repository, Git allows developers to copy the whole repository to their own system so that when a change is made to the local copy, that change is easily pushed to the central server.
This way, there will be no need for the dev to make a new server connection for every single change they make.
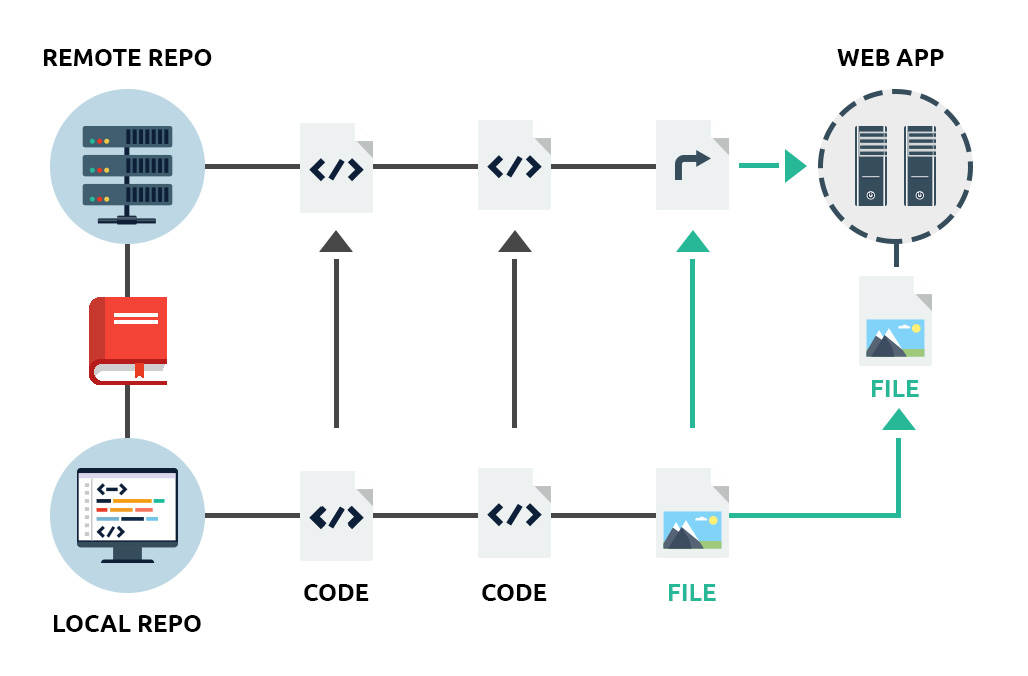
What is Git mostly used for?
Most often, a developer would use Git to set up preview versions of the website or application they are working on to test them out on the production server, or even on a different test/staging server.
To use Git on a web server for testing purposes, a developer will need to first create a Git repository on their local machine and then set up a cloned Git repository on the server.
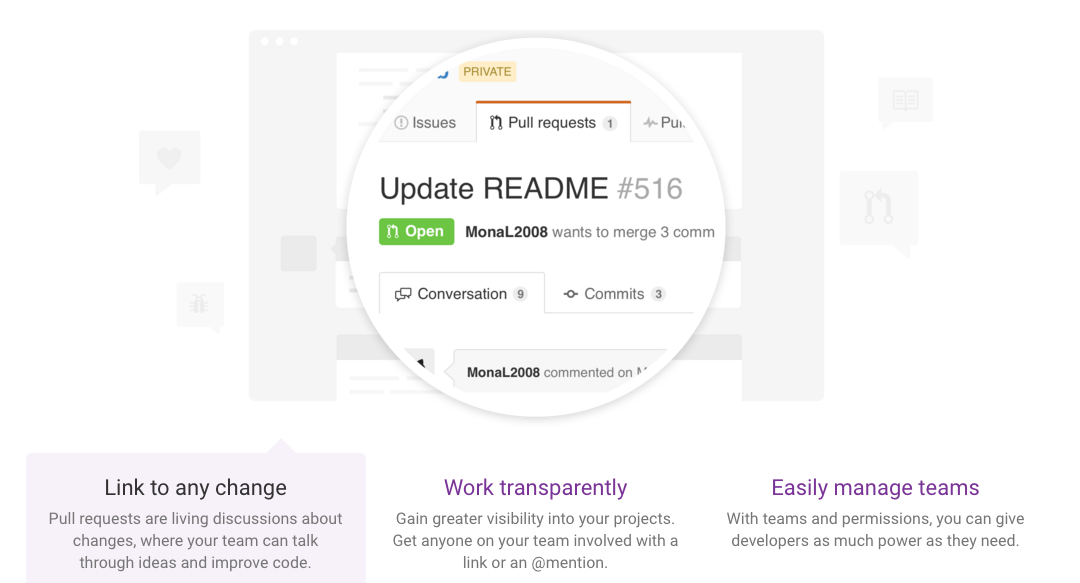
Using Git repository hosting platforms like GitHub, developers can test their projects in a web-based graphical environment:
With Git enabled on our web hosting platform, developers will be able to push, pull or clone their projects from GitHub, or any other platform that’s hosting their repository, to one or more web hosting accounts on our servers.
This is all best done over SSH, which opens a secure connection and executes Git operations on the server as required.
The use of SSH eliminates the need for deploying a daemon service on the server to push requests, which is one of the main security concerns of web hosts.
Using Git to deploy a simple script or an entire app on a web hosting server is a fast and easy way to spread that version controlled content over a few web hosting accounts at the same time.
This will save developers all the hassle of uploading the content to all the accounts successively over FTP. The same holds true for updates – instead of having to use FTP to upload script or app updates to each web hosting account separately, the developer will just need to push an update from the Git repository with a simple Git+SSH command.
How to create a Git repository on a web server?
With Git now supported on our web hosting platform, you will be able to create your own repository directly on the server where your websites are located, instead of using third-party services like GitHub.
First of all, you will need to have SSH access enabled for your web hosting account.
We include SSH access by default with the Enterprise plan, the Semi-dedicated 2 plan and with all VPS and dedicated server solutions on our platform.
With all other packages, SSH is available as an upgrade.
Example Usage
Here, we’ll examine a very basic Git repository usage scenario that will allow us to track and deploy a local (as in residing on our workstation) copy of a dev app in our production environment on the hosting web server.
Step 1: Prepare the remote (web server) Git and SSH environments
Let’s assume that our production app directory resides in ~/www/my-domain.tld/ and that our Git repository is located in ~/git_repos/my_app/.
We need to execute the following in our web server environment:
$ ssh username@my-domain.tld -p 2222After you supply your password and are logged in, you may proceed with:
$ mkdir -p ~/git_repos/my_app
$ cd ~/git_repos/my_app
$ git init
This will initiate the Git repository and will allow us to take advantage of all the ‘goodies’ that the Git tool suite provides.
Now we need to tell Git to accept pushes to our working directory (~/www/my-domain.tld/):
$ git config receive.denyCurrentBranch ignore
The next step is to create a post-receive hook that will help us deploy my_app’s code directly into our working directory:
$ editor_of_your_choice ~/git_repos/my_app/.git/hooks/post-receiveFill the file with the following contents:
#!/bin/sh
GIT_WORK_TREE=~/www/my-domain.tld/ git checkout -fSave it and make the hook file executable:
$ chmod 0750 ~/git_repos/my_app/.git/hooks/post-receiveAnd a small step that will help us set up SSH:
$ mkdir -m 0700 ~/.ssh/
$ touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysStep 2: Prepare the local (workstation) Git and SSH environments
Let’s assume that the app you’re developing resides in ~/projects/my_app/ and contains only one example file: index.php – we’ll set up a Git repository in the same directory:
$ cd ~/projects/my_app/
$ git init $ git add index.php
$ git commit -m 'initial version'
$ git remote add origin username@my-domain.tld:git_repos/my_appWe need to generate a cryptographically strong SSH public/private key pair:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096This will create two files: ~/.ssh/id_rsa (private key) and ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub (public key).
Create a ~/.ssh/config file and add the remote host info:
Host my-domain.tld
Port 2222
PreferredAuthentications publickey,passwordIf you already have this file, you only need to update it using the information above.
Now add the SSH public key to the production environment:
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh username@my-server.tld "cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"Step 3: Deploy your app’s code to production
Now we only need to push my_app’s code into production via Git:
$ git push -u origin master.That’s it! Your app (index.php in this example) is now deployed on the remote web server in the ~/www/my-domain.tld/ directory.
—
Git is enabled by default with all Hepsia Control Panel-managed hosting solutions including:
- Web hosting packages
- Semi-dedicated servers
- OpenVZ Virtual Private Servers with a Hepsia installation
- Dedicated servers with a Hepsia installation
On your hosting stores, Git support is listed as a feature in the plan tables under Databases, Scripting and Development:

Tags: Hepsia control panel, scripting


Leave a Reply