An option to configure disks in RAID added for dedicated server users
Just a month ago, we launched a fully revamped line of SSD-based dedicated servers to give you a new competitive edge on the advanced hosting market.
Also, we implemented storage configuration options to add a new level of flexibility to the server setups.
To take the level of server configuration control even further, we’ve now added an option that allows users to use disks in a RAID configuration and thus increase the efficiency of their machines.
What does RAID stand for?
RAID stands for “Redundant Array of Independent Disks” and allows multiple disks to act as a single entity.
The RAID technology is usually aimed at accomplishing improved reliability and better performance for dedicated server-hosted projects.
Plus, combining multiple disk drives into a single unit could help increase storage capacity.
Usually, RAID employs the technique of either disk mirroring, disk striping, or a combination of both.
Disk striping involves partitioning a drive’s storage space into smaller units that are distributed over several disks.
The data is then read from all the disks at the same time, which means better performance in comparison with the single disk scenario.
Disk mirroring means creating an exact copy of all the data on a given disk and replicating it to another disk.
Whenever there is a change, it gets reflected on both disks.
This ensures high redundancy, as even if there is a problem with one of the disks, its mirror disk can pick up the load instead.
What are the new RAID configuration options about?
Through the possibility to arrange disks in a RAID configuration, your customers will be able to improve the way their data is served to the audience.
Depending on the goal you want to achieve and the projects you are running, there are different RAID configurations to choose from.
They are usually designated with the word “RAID” and a number to indicate the specific configuration in which the disks are arranged.
Here are the RAID scenarios that your customers will be presented with at signup:
RAID 0 – the data is split evenly across the available disks.
This scenario brings excellent performance, but offers no redundancy. At least two disks are required:
Recommended for: testing environments;
Not good for: systems that are vulnerable to data loss;
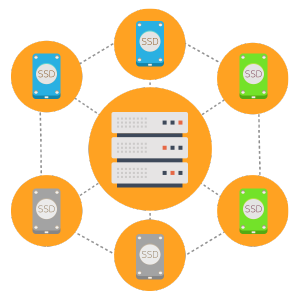
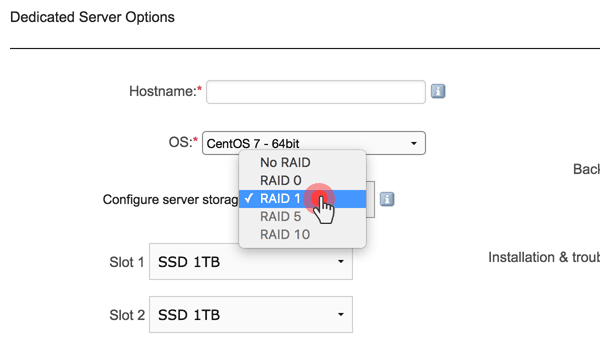
RAID 1 – also known as “disk mirroring”, i.e. replicating data from one disk to another.
This scenario offers excellent redundancy where the read performance is improved, since either disk can be read at the same time, while the write performance is the same as the one offered by the single disk storage scenario. At least two disks are required to duplicate the storage of data:
Recommended for: projects where data safety is of critical importance;
Not good for: projects that rely on high I/O speeds;
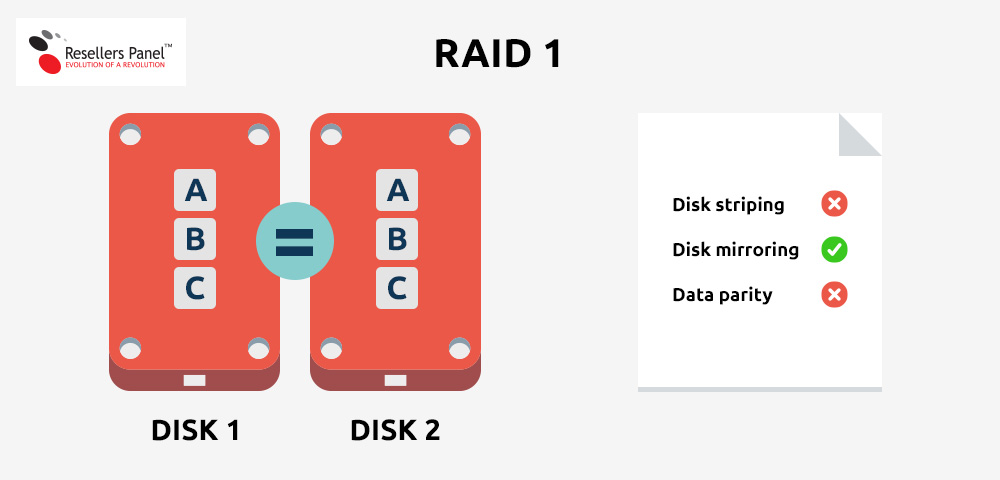
RAID 5 – the data is split evenly across the disks, with each disk containing information about what data is stored on the other disks.
This scenario allows the array to operate even if one of the drives fails. It yields good redundancy results and provides better performance in comparison with the single drive storage scenario, but not as good as that offered by the RAID 0 array. RAID 5 requires at least three disks:
Recommended for: all types of static content; WordPress-driven sites that rely on databases for content storing purposes;
Not good for: any projects that require regular content changes;
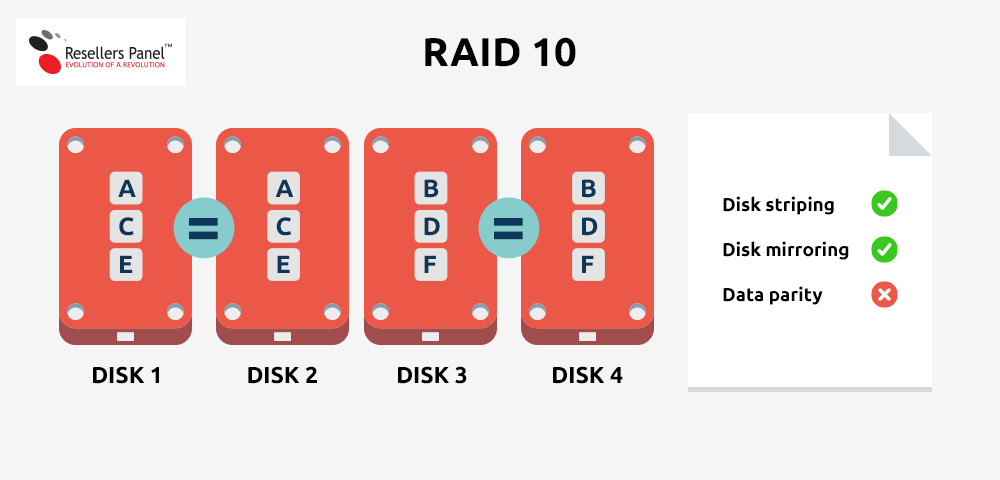
RAID 10 – the data is split evenly across the available disks, with each disk having a mirror disk. This scenario combines RAID 1 and RAID 0 (RAID 1+0) and offers excellent performance and redundancy. Four or more disks are required as their number has to be even, i.e. 4, 6, 8, etc.
Recommended for: any mission-critical applications, especially database-driven ones;
How does the RAID configuration option work?
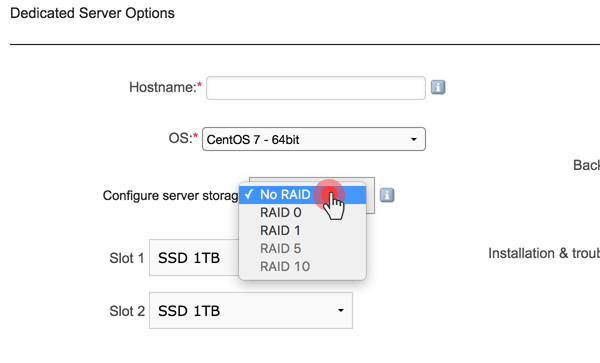
When a customer selects a dedicated server on the order form, they will be presented with the option to select how they want their storage to be configured.
If they want to go with a normal disk setup, they should select “NO RAID” from the drop-down menu:
If they want to order RAID-configured disks, then they should opt for any of the 4 available RAID options:
NOTE: To take advantage of the new RAID configuration options, you will need to use drives of the same type and storage capacity.
Originally published Friday, July 15th, 2016 at 1:16 pm, updated July 8, 2024 and is filed under Dedicated Servers.Tags: dedicated servers


Leave a Reply